Prompt Engineering has taken the world by storm, with everyone eagerly discussing its significance in generative AI. It is undoubtedly the latest focus in natural language processing (NLP) technologies, such as OpenAI’s GPT series. Through experimentation, developers and users have realized that the quality, accuracy, and relevance of AI-generated content largely depend on how input prompts are crafted. Consequently, prompt engineering has evolved into a distinct field, giving rise to a new professional role – prompt engineers, who are in demand.
However, being able to tap into the true potential of generative AI extends far beyond the art of creating effective prompts. Above all, it requires human skills: proficient strategic and creative thinking anchored in clear objectives and goals, along with expertise for validating and fine-tuning the output through an iterative process. Depending on the task, a careful curation and adjustment of generated content is mostly indespensable. In addition, humans possess emotional intelligence, an innate ability to empathize and understand their audience, deliver genuine value, and stir emotion-essential skills for creating compelling, winning content.
In this short article, we will look at good prompt engineering, share valuable tips and some best-practice examples, and demonstrate how adept prompt engineering can support healthcare article writing.
The prompt engineering foundation
A basic understanding of AI language models is crucial in creating well-crafted and impactful prompts. Consider large language models (LLMs) and generative AI as sophisticated prediction engines that, when prompted, generate a response by sequentially choosing words based on their likelihood to follow. That means they select one word at a time from words that are likely to come next. These models are just math functions, so they cannot think. Although it is a bit more complex (or more straightforward, depending on how you look at it), this viewpoint helps occasional users grasp the core concept.
If you seek to advance, start by understanding AI learning algorithms and familiarize yourself with one-shot, zero-shot, and few-shot learning concepts, for instance here. Few-shot prompting (showing the model a few examples, called shots) in particular has been associated with better results. Such knowledge allows you to craft prompts that produce an optimal prediction performance (output) and improves your ability to assess the result for quality and relevance more critically.
Other areas worth investigating include tokenization, context window, and attention mechanism. For those interested, read the medium article of Anthony Pece here or explore more on learnprompting.org.
What is a good prompt?
A prompt is no more but a request, a query, or a set of instructions provided to the generative AI model to trigger a response—the more detailed and structured this request or prompt, the better and more concise the output.
For example, if you want to write an article about the benefits of exercise for mental health, you could use this simple prompt:
`Write an article about how exercise can improve mental health.`
As you can imagine, without more detail, this article could be anything, from 5 sentences to 10 pages of unspecific, random, wordy and unstructured information (that no one is really interested in).
As a general rule of thumb, avoid open-ended or broad requests like the above example for a specific task such as article writing. Always narrow the instructions down.
An example of an elaborated prompt for BingChat for the same article could look like so:
`Write an article about how exercise can improve mental health. Use the following structure:
- Introduction: Explain what mental health is and why it is important. Provide some statistics on the prevalence and impact of mental health problems. State your main argument that exercise can help prevent and treat mental health problems.
- Body: Discuss at least three benefits of exercise for mental health, such as reducing stress, improving mood, and enhancing cognitive function. Provide evidence from scientific studies and reputable sources to support your claims. Use appropriate terminology and cite your sources using APA style.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your argument. Provide some practical tips on how to incorporate exercise into daily life. End with a call to action or a question for further discussion.
Use a clear, concise, and engaging tone. Write at least 750 words but not more than 1200.`
This example prompt still misses important details such as your role or specifications for the target audience. It also misses clear guidelines for generating suitable headings and sub-headings and lacks examples to guide the model’s learning (few-shot). To elevate the prompt’s effectiveness, incorporating instructions for engaging the user could foster a more conversational experience and enable the model to produce improved responses.
Best practice – Megaprompts and Iteration
Don't be afraid of Megaprompts
Before it gets too complex, let’s revisit the so-called Megaprompts. As defined in a previous blog article a Megaprompt for a text-to-text model should include the following information (and possibly more):
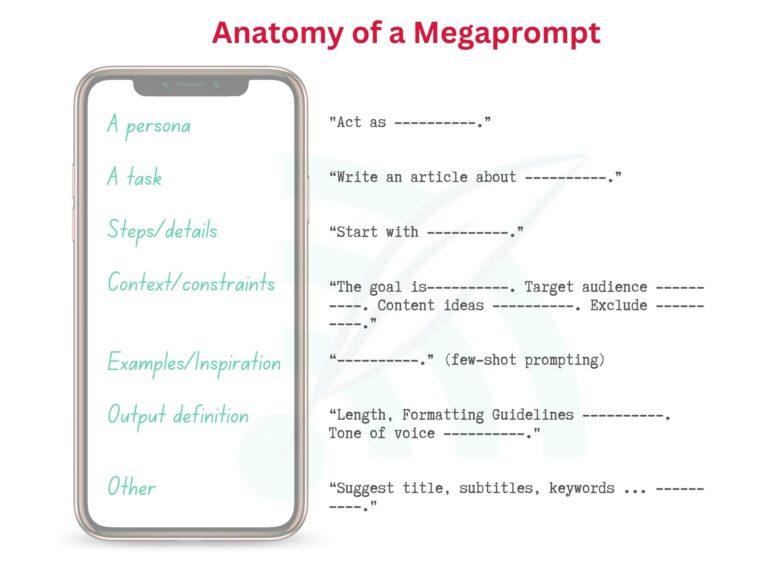
There is no rule or gold-standard how to write and organize your prompts, so you are free to experiment around. Whatever works best for your project is fine. Trial and error is the best way to learn.
You could even use your AI model to help you create or improve your prompts. There is a good example of using ChatGPT as promptengineer on Reddit. You can access it here and adapt it to your needs.
Well-defined prompts ensure that the conversation stays on track and returns information that is relevant and more accurate, resulting in an engaging and informative experience.
Iterative process of refining prompts
Prompt engineering as a strategic and creative endeavor involves trial and error testing, which means experimenting and refining based on the returned results. This way, your model learns and can potentially return more satisfactory results.
A good practice for improving a model’s performance is using a stepwise approach. There are various ways of doing it, which most of you have already applied without even thinking about it:
- Refine through re-prompting the passages that need clarification or revision
- Incorporate instructions for a stepwise approach upfront into the Megaprompt
- Chain of thought (CoT) prompting
Example prompts for CoT:
`Let’s think step by step… /Let’s work this out step by step to be sure we have the right answer …`
`Ask questions before answering to understand better what I am looking for. Explain your suggestion step by step. Is that understood?`
To go back to our example article about the benefits of exercise for mental health, a megaprompt for BingChat could be as follows:
`Please ignore all previous instructions and prompts.
Act like a medical writer commissioned to write an article about how exercise can improve mental health. The article will be published as a blog post on a psychotherapist’s private practice website who is seeing adults. It will be distributed as part of the next email newsletter.
Use the following structure:
- Introduction: Explain what mental health is and why it is important. Provide some statistics on the prevalence and impact of mental health problems. State your main argument that exercise can help prevent and treat mental health problems.
- Body: Discuss at least three benefits of exercise for mental health, such as reducing stress, improving mood, and enhancing cognitive function. Provide evidence from five scientific studies and reputable sources to support your claims. Use appropriate terminology and cite your sources using APA style.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your argument. Provide some practical tips on how to incorporate exercise into daily life. End with a call to action or a question for further discussion.
Use a clear, concise, and engaging tone. Write at least 750 words but not more than 1200. Write in UK English for 9th-graders.
Please, do not echo my prompt. Do not remind me what I asked you for. Don’t use generic filler sentences. Do not hallucinate.
Please use the keyword “exercise and mental health”. Suggest a compelling title and useful keyword-rich subheadings. When you have generated the article suggest two additional titles and two alternative keywords.
Do not end this session until I choose to end it. Await further instructions. Thank you.`
Although not perfect, as the example/inspiration is still missing, this promptversion offers more information and guidance that will help the model produce more specific and relevant output. And most importantly, it considers and provides context.
Also, take note of the small tweaks, such as 👉🏻“Please, do not echo my prompt. Do not remind me what I asked you for. Don’t use generic filler sentences. Do not hallucinate,”👈🏻which have proven to be quite useful.
Saving your prompts will save you time
When experimenting with different prompts and iterations, you’ll certainly discover a few well-crafted ones that work exceptionally well. Make the most of these by saving them separately for easy access, even hough they’re stored in your AI model accounts. This gives you more flexibility and control.
Use Excel Sheets or Google Docs to create a centralized repository where you can organize both your own and others’ prompts into categories, add notes, and track their performance. For a more tailored solution, consider using dedicated apps or extensions like PromptBox or ChatGPT Prompt Genius.
These applications are designed specifically for organizing and managing prompts, streamlining your workflow, and making prompt storage and retrieval even more efficient. Moreover, storing prompts separately makes sharing your collection with your team seamless, fostering a collaborative environment and accelerating the growth of your team’s AI language model proficiency.
Moving forward in synergy
The success of generative AI relies heavily on the human touch. Only by refining your prompt engineering skills, understanding AI language models, and consistently implementing best practices can you harness the full potential of these innovative tools to enhance your workflows. Keep in mind that human skills, such as creativity and strategic thinking, are paramount for guiding AI models to produce specific and relevant output. Additionally, only human adaptation of the output can ensure the creation of accurate, relevant, and compelling content that resonates with your audience. Embracing the synergy between human expertise and generative AI capabilities paves the way for boundless possibilities. Prompt Engineering Skills are here to stay 👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻.